
He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. During times of recession, however, it may cause serious cash flow problems. DOL is based on historical data and may not accurately predict future performance. Additionally, it does not consider the impact of external factors like market conditions and economic changes.
- So, while operating leverage is a good starting point for an analysis, it gives you an incomplete picture unless you also consider overall margins and industry dynamics when comparing companies.
- Under all three cases, the contribution margin remains constant at 90% because the variable costs increase (and decrease) based on the change in the units sold.
- In fact, financial leverage relates to financing activities (i.e., the cost of raising funds from different sources carrying fixed charges or not involving fixed charges).
- After its breakeven point, a company with higher operating leverage will have a larger increase to its operating income per dollar of sale.
- High DOL indicates that a small percentage change in sales can lead to a significant change in operating income.
How Does Operating Leverage Impact Break-Even Analysis?
Managers need to monitor DOL to adjust the firm’s pricing structure towards higher sales volumes as a small decrease in sales can lead to a dramatic decrease in profits. Despite the significant drop-off in the number of units sold (10mm to 5mm) and the coinciding decrease in revenue, the company likely had few levers to pull to limit the damage to its margins. However, the downside case is where we can see the negative side of high DOL, as the operating margin fell from 50% to 10% due to the decrease in units sold. If revenue increased, the benefit to operating margin would be greater, but if it were to decrease, the margins of the company could potentially face significant downward pressure. If a company has high operating leverage, each additional dollar of revenue can potentially be brought in at higher profits after the break-even point has been exceeded.
Financial Leverage
Here’s your step-by-step guide to using the Degree of Operating Leverage Calculator. Finally, it is essential to have a broad understanding of the business and its financial performance. That’s why we highly recommend you check out our otherfinancial calculators. We will need to get the EBIT and the USD sales for the two consecutive periods we want to analyze. For torrance, ca income tax preparation, cpa and irs enrolled agent the particular case of the financial one, our handy return of invested capital calculator can measure its influence on the business returns. We saw this with airlines during COVID-19 and the travel restrictions that took effect in 2020; many airlines had to be bailed out due to greatly reduced ticket sales and their low Cash balances and poor liquidity ratios.
What are the benefits and risks involved in using financial leverage?
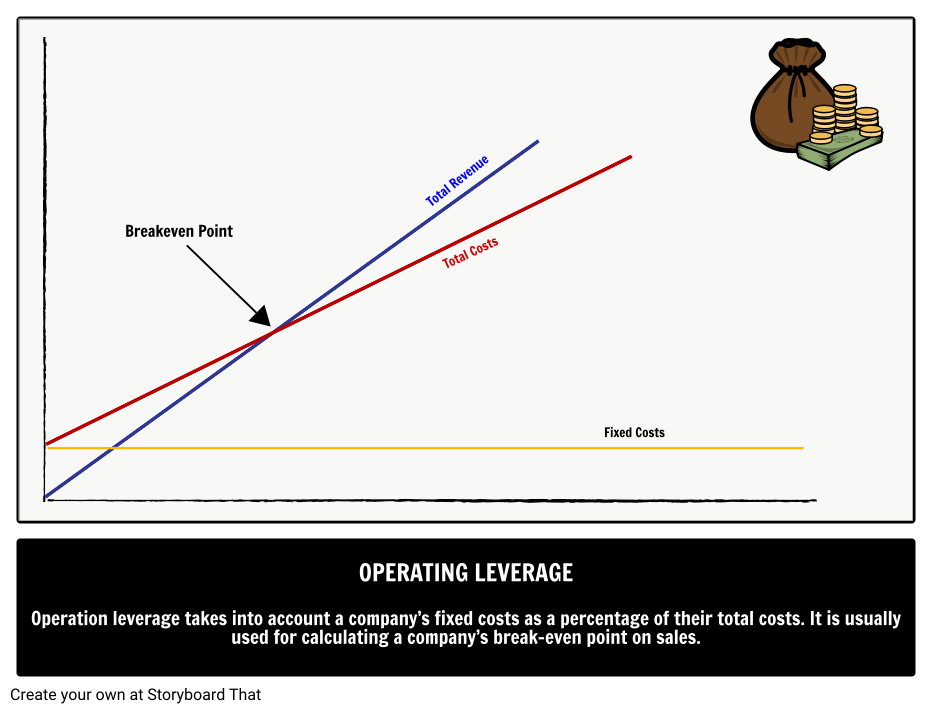
Operating leverage measures a company’s fixed costs as a percentage of its total costs. It is used to evaluate a business’ breakeven point—which is where sales are high enough to pay for all costs, and the profit is zero. A company with high operating leverage has a large proportion of fixed costs—which means that a big increase in sales can lead to outsized changes in profits. A company with low operating leverage has a large proportion of variable costs—which means that it earns a smaller profit on each sale, but does not have to increase sales as much to cover its lower fixed costs.
This formula is useful because you do not need in-depth knowledge of a company’s cost accounting, such as their fixed costs or variable costs per unit. From an outside investor’s perspective, this is the easier formula for degree of operating leverage. It simply indicates that variable costs are the majority of the costs a business pays. While the company will earn less profit for each additional unit of a product it sells, a slowdown in sales will be less problematic becuase the company has low fixed costs. The high leverage involved in counting on sales to repay fixed costs can put companies and their shareholders at risk. High operating leverage during a downturn can be an Achilles heel, putting pressure on profit margins and making a contraction in earnings unavoidable.
What Is the Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL)?
Indeed, companies such as Inktomi, with high operating leverage, typically have larger volatility in their operating earnings and share prices. By breaking down the equation, you can see that DOL is expressed by the relationship between quantity, price and variable cost per unit to fixed costs. If operating income is sensitive to changes in the pricing structure and sales, the firm is expected to generate a high DOL and vice versa. If the composition of a company’s cost structure is mostly fixed costs (FC) relative to variable costs (VC), the business model of the company is implied to possess a higher degree of operating leverage (DOL). Operating Leverage is a financial ratio that measures the lift or drag on earnings that are brought about by changes in volume, which impacts fixed costs. Many small businesses have this type of cost structure, and it is defined as the change in earnings for a given change in sales.
As a hypothetical example, say Company X has $500,000 in sales in year one and $600,000 in sales in year two. In year one, the company’s operating expenses were $150,000, while in year two, the operating expenses were $175,000. The only difference now is that the number of units sold is 5mm higher in the upside case and 5mm lower in the downside case. Companies with high DOLs have the potential to earn more profits on each incremental sale as the business scales.
Conversely, Walmart retail stores have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because Walmart sells a huge volume of items and pays upfront for each unit it sells, its cost of goods sold increases as sales increase. Other company costs are variable costs that are only incurred when sales occur. This includes labor to assemble products and the cost of raw materials used to make products. Some companies earn less profit on each sale but can have a lower sales volume and still generate enough to cover fixed costs.
But companies with a lot of costs tied up in machinery, plants, real estate and distribution networks can’t easily cut expenses to adjust to a change in demand. So, if there is a downturn in the economy, earnings don’t just fall, they can plummet. In contrast, a company with relatively low degrees of operating leverage has mild changes when sales revenue fluctuates. Companies with high degrees of operating leverage experience more significant changes in profit when revenues change. Financial and operating leverage are two of the most critical leverages for a business.

